The Social Thinking Methodology has been a guiding resource for schools, clinics, individuals, and families around the world for more than 25 years. Our work supports individuals' social, emotional & academic learning, whether neurotypical or Neurodivergent, with or without diagnosis. Our materials are helpful for students with solid to strong expressive and receptive language skills in mainstream and special education. They can be used across developmental ages to support the development of social competencies, flexible thinking & social problem solving to improve: conversation & social connection, executive functioning, friendship & relationship development, perspective taking, self-regulation, and Social Thinking Vocabulary. Help us protect the fidelity of this body of work and be informed about how you can/can’t use our materials considering our intellectual property, copyrights and trademarks.
- Products for All Ages
- Visual Supports
- Online Training
- Free Webinars
- Article Library
- Digital Products

Products for All Ages
Teachers, speech-language pathologists, clinicians, behavior specialists, and parents are using our expansive collection of curricula, books, games, and posters to teach social competencies to social learners ages 4 and up.
While our deeper work is for individuals with social learning differences and/or challenges (ADHD, twice exceptional, social communication differences, autism spectrum levels 1 and 2, and other social, emotional, and cognitive learning differences (with diagnoses or without), our work is also being adopted into mainstream classrooms and workplaces around the world to improve social, emotional, and academic learning for all.

Posters, Games & Visual Supports
Our visual supports provide a fun, engaging way for your students to learn about their own thoughts, feelings, and reactions and of those around them. With powerful visual supports students can more easily connect with social concepts and apply them to their own lives. As an added bonus, our visual supports are versatile and can be used in a variety of settings from the classroom or clinic to your home.
Spark student engagement & raise social awareness—there’s something for everyone.
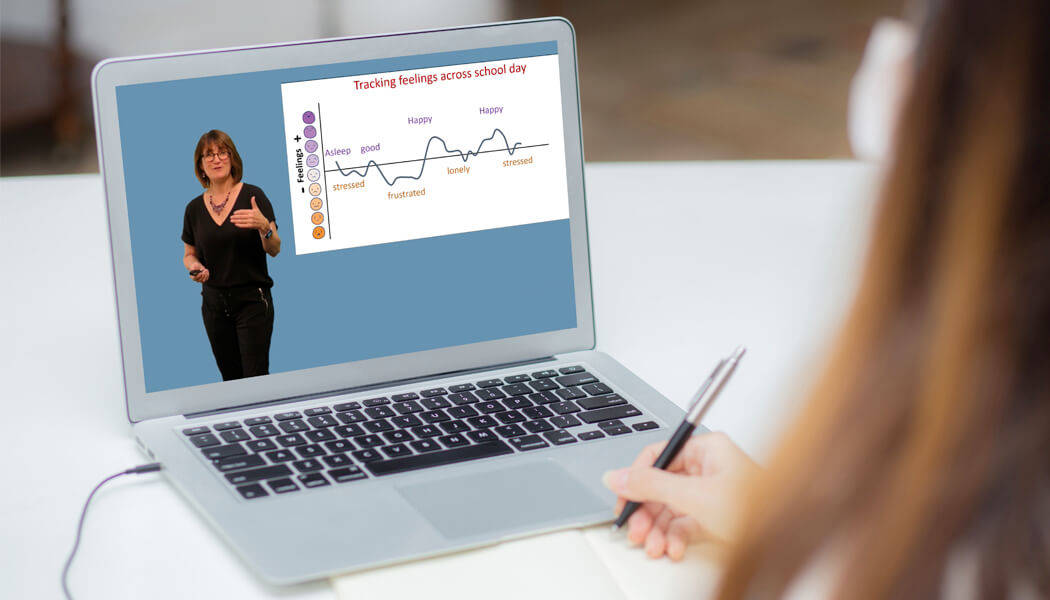
Online Training
Utilizing more than 25 years of clinical practice and the latest research, these one-of-a-kind online training courses explore a large range of aspects required for developing social competencies, including self-regulation, executive functioning, social problem-solving, and much more. These courses have been watched and raved about over 50,000 times from all around the world!
This is your opportunity for deeper learning and to earn CE Credit (for select professionals).

Free Webinars
Explore how to teach a variety of core Social Thinking concepts—for free. Browse our entire webinar collection and discover strategies to help people of all ages develop social competencies, self-regulation, social skills, social-emotional understanding, flexible thinking, and more!
Our webinars are not pre-approved for credit by continuing education organizations. However, all participants can download and print a Certificate of Completion.

Article Library
Social Thinking is proud to provide an extensive collection of free articles devoted to helping individuals build stronger social awareness and social functioning using the Social Thinking Methodology.
Browse our library of 100+ free articles and learn strategies you can start using right away. We’re constantly adding material based on the latest research and our evolving client work—so visit our library often and stay informed!

Digital Products
Our newest and most popular digital products make it easy for children to explore social emotional learning.
Build social awareness and vocabulary with our award-winning You Are A Social Detective, Social Thinking and Me & Superflex curriculum.
Teach strategies to help students better problem solve & self-regulate with our all new Social Thinking Frameworks collection.
Best-Selling Series
Browse by Age
Practical Strategies Taught by Thought Leaders
Our Newest Webinars
Must-Read Articles
Digital Curricula, Storybooks & Visual Supports

There are 3 distinct yet overlapping definitions:
What do we mean when we say, "social thinking?" We have a lot of information to share. Here are three ways to understand how we use the words "social thinking:"
- The Term
- The Business
- The Methodology
Watch the video or browse below to learn more!

Over time, our teachings can help people cultivate relationships and improve performance at school and at work. For 25 years our experts have been a guiding resource for schools, clinics, and families around the world, and we’re here for you, too. Whether you're teaching individuals with ADHD, autism spectrum (levels 1 or 2), social communication disorders, or an entire mainstream class-our strategies can help you help them.
This has been a game changer for helping general education teachers. We have been using the Social Thinking Methodology with our students, they are making friends, are more successful academically, and generally happier in all they do. Thank you! - Jennifer, Special Education Teacher
The Social Thinking Training and Speakers' Collaborative (STTSC) consists of 13 clinicians, including Michelle Garcia Winner and Dr. Pamela Crooke, who train around the world on the Social Thinking Methodology in addition to working closely with schools, clients, and families. All of our speakers have an active caseload and provide training to help schools embed Social Thinking’s teachings across all aspects of the educational day in public and private schools. We also work with universities as well as businesses to help adults continue to develop stronger social communication skills. Please note that the members of our STTSC are the only people licensed and approved to give training on the Social Thinking Methodology.
The speaker did an excellent job at keeping our attention and broke the information down in a way that was easy to understand and gave us a process to help ensure we could implement what we learned.
- Special Ed. Teacher, School Training


Personalized Training for Your School or Clinic

Strategies to Build Social Competencies
The Social Thinking Methodology provides evidence-based strategies to help people ages four through adult develop their social competencies, flexible thinking & social problem solving to meet their own social goals and improve:
- Conversation & social connection
- Executive functioning
- Friendship & relationship development
- Perspective taking
- Self-regulation
- Social Thinking Vocabulary